报告错误
如果你发现该网页中存在错误/显示异常,可以从以下两种方式向我们报告错误,我们会尽快修复:
- 使用 CS Club 网站错误 为主题,附上错误截图或描述及网址后发送邮件到 286988023@qq.com
- 在我们的网站代码仓库中创建一个 issue 并在 issue 中描述问题 点击链接前往Github仓库
前提条件
使用场景
线段树的应用场景与二进制索引树相似,当我们需要多次查询数组子区间的特性/数据并同时高效修改数组内容的时候,我们可以使用线段树。
线段树并不是一种单一的数据结构 - 它代表了一类具有相同思想方法的数据结构 - 通过二叉树做到区间内容的高效查询,这里的内容可以是区间最大/最小值,区间和,等等 。
数据结构
线段树是一个二叉树,线段树中的每一个节点代表序列中的一个区间。假设对于 长度为 $N$ 的 array $A$,我们有对应的线段树 $T$,那么……
- $T$ 的根节点代表整个 array $A$
- $T$ 的每个叶子节点都代表 array $A$ 中的一个值 $A[i]$,$0\leq i\lt N$
- $T$ 中的每一个非叶节点都代表 array $A$ 的一个子序列 $A[i:j]$,$0\leq i\lt j \lt N$
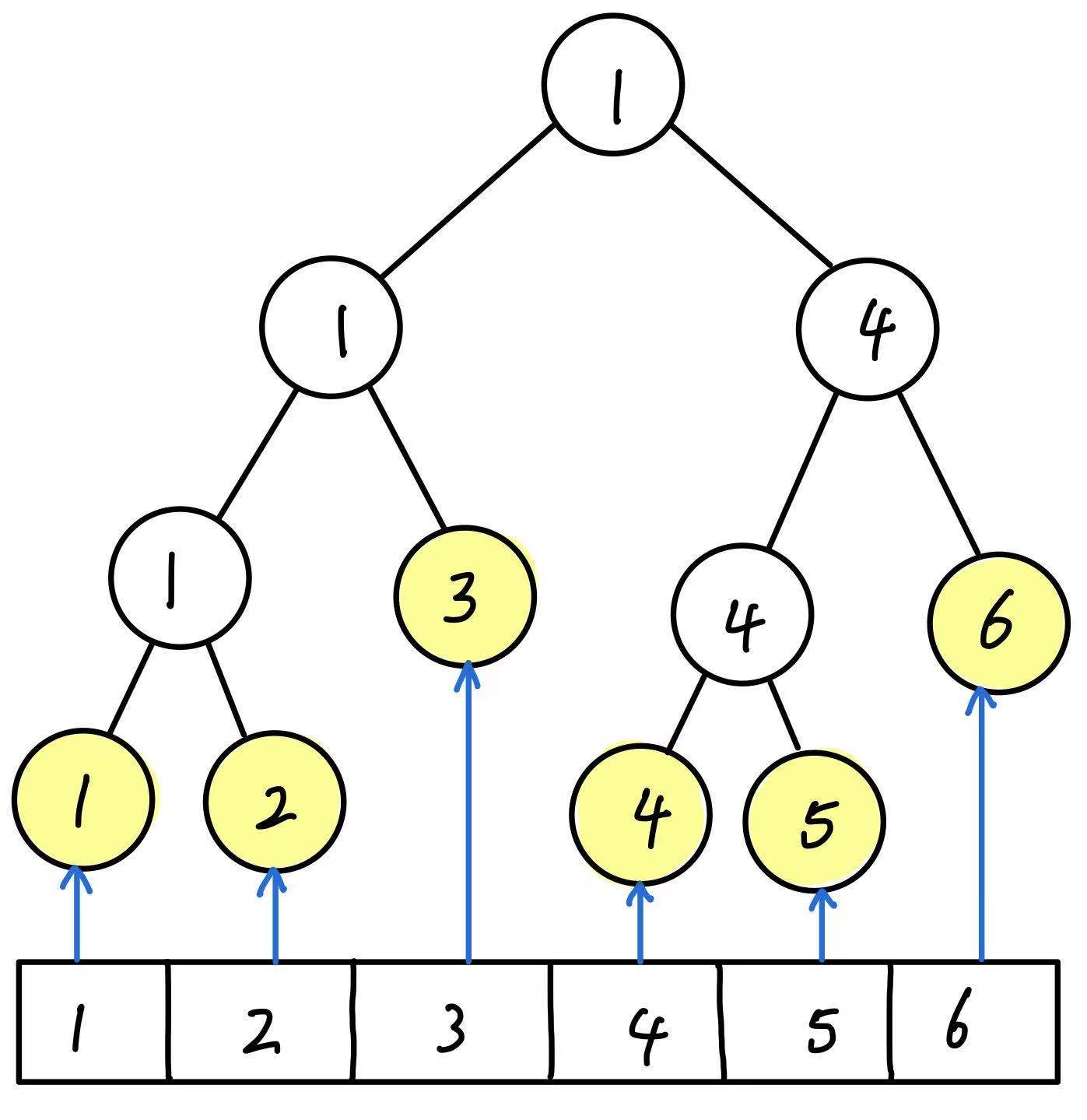
在一个线段树中,所有的叶子节点一定代表原数组中的一个值
注意线段树不一定是满二叉树
时间复杂度
初始化复杂度 - $O(n)$
对于一个长度为 $n$ 的 array,对应的线段树中最多一共有 $2n + 1$ 个节点。每个节点的初始化都是 $O(1)$ 的时间复杂度,所以线段树的初始化复杂度是 $O(n)$。
更新复杂度 - $O(\log{n})$
对于一个长度为 $n$ 的 array,每次修改一个单一的值需要修改这个节点的所有父节点与“祖先节点”(例如父节点的父节点,父节点的父节点的父节点……)。对于一颗线段树,最多有 $\log_2{n}$ 的高度,所以更新一次线段树的值的时间复杂度是 $O(\log_2{n}) = O(\log{n})$
查询复杂度 - $O(\log{n})$
查询节点数量最多的情况出现于查询 $[l, l]$ 时,这时候我们需要从根节点一路递归的遍历到叶子节点,一共遍历 $O(\log{n})$ 个节点。所以查询区间的时间复杂度是 $O(\log{n})$
Java实现
一个线段树有三个主要的方法:
- 初始化(Constructor)- 给定一个 Array,构建这个 Array 对应的线段树
- 查询 (Query)- 给定一个区间范围 $[l, r]$,返回这个区间的信息(最大值,最小值,和 etc)
- 更新 (Update)- 给定 index $i$ 与新的值 $v$,更新线段树
下面,我们会实现一个基于 范型 (Generic Type) 的最小线段树。对于任意实现了 Comparable 接口的类型 T 的 ArrayList<T>,我们都可以使用这个线段树来求出区间 $[l, r]$ 中的最小对象 $T$。
Helper Functions
在正式实现线段树前,我们先写一些后面可以用到的 Helper Functions。
-
genericMin函数通过比对T.compareTo的值来返回两个T对象中较小的一个对象 -
getLChild计算出当前节点的左子节点的 index -
getRChild计算出当前节点的右子节点的 index -
inInterval计算出区间 $[l1, r1]$ 和 $[l2, r2]$ 之间的关系
public class SegmentTree <T extends Comparable<T>>{
private ArrayList<T> tree;
private T[] value;
private int getLChild(int index){ return index * 2 + 1; }
private int getRChild(int index){ return index * 2 + 2; }
private T genericMin(T o1, T o2){
if (o1.compareTo(o2) > 0){ return o2; }
return o1;
}
private int inInterval(int l1, int r1, int l2, int r2){
if (r2 < l1 || l2 > r1){ return 0; } // Intervals do not have any intersection
else if (l2 >= l1 && r2 <= r1){ return 1; } // Interval 2 complete in Interval 1
else{ return 2; } // Interval 2 partially intersect with Interval 1
}
}
注意我们的 tree 属性使用的是 ArrayList 而不是 array
这是因为 Java 中不能创造 Generic Type Array
Construct Segment Tree
我们使用递归的方法来构建线段树 - 根节点的范围是 $[0, arr.length - 1]$,计算出中间的节点 $mid = (arr.length - 1) / 2$,左节点的范围就是 $[0, mid]$,右节点的范围是 $[mid + 1, arr.length - 1]$。
当节点的范围是 $[l, r]$ 且 $l = r$ 时,节点的值就是 Array 中对应元素的值 - 此时这个节点时叶子节点。
public SegmentTree(T[] values){
this.tree = new ArrayList<>(Collections.nCopies(values.length * 2 + 1, null));
this.value = values;
this.constructTree(0, 0, values.length - 1);
}
private void constructTree(int node, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) {
tree.set(node, value[l]);
} else {
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
this.constructTree(this.getLChild(node), l, mid);
this.constructTree(this.getRChild(node), mid + 1, r);
tree.set(node, this.genericMin(tree.get(this.getLChild(node)), tree.get(this.getRChild(node))));
}
}
Update Segment Tree
类似的,我们在更新 Segment Tree 时也使用递归的方法更新 - 如果要修改的 index 在当前节点的范围内,我们就递归的修改下一层,最后再 bottom-up 的更新整条路径上的 $O(\log{n})$ 个节点
public void updateTree(int index, T val){
this.updateTree(0, 0, this.value.length - 1, index, val);
}
private void updateTree(int node, int l, int r, int index, T val){
if (l == r){
this.tree.set(node, val);
this.value[l] = val;
}
else{
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (l <= index && index <= mid){ this.updateTree(this.getLChild(node), l, mid, index, val); }
else{ this.updateTree(this.getRChild(node), mid + 1, r, index, val); }
this.tree.set(node, this.genericMin(this.tree.get(this.getLChild(node)), this.tree.get(this.getRChild(node))));
}
}
Query Interval Minimum
在查询线段树中的区间最小值时,我们把所有情况分为三种:
- 当前节点代表的区间完全在查询的区间内
- 当前节点代表的区间部分在查询的区间内
- 当前节点代表的区间完全不在查询的范围内
对这三种情况,我们采取不同的动作
| 情况 | 操作 |
|---|---|
| 节点区间完全在查询区间内 | 返回当前节点的值 |
| 节点区间部分在查询区间内 | 继续向下递归,返回左节点与右节点返回值的较小值 |
| 节点区间完全不在查询区间内 | 返回 null
|
public T queryMin(int l, int r){
return queryMin(0, 0, this.value.length - 1, l, r);
}
private T queryMin(int node, int start, int end, int l, int r){
if (this.inInterval(l, r, start, end) == 0){ return null; }
else if (this.inInterval(l, r, start, end) == 1){ return this.tree.get(node); }
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
T leftInterval = this.queryMin(this.getLChild(node), start, mid, l, r);
T rightInterval = this.queryMin(this.getRChild(node), mid + 1, end, l, r);
if (leftInterval == null){ return rightInterval; }
else if (rightInterval == null){ return leftInterval; }
else{ return this.genericMin(leftInterval, rightInterval); }
}
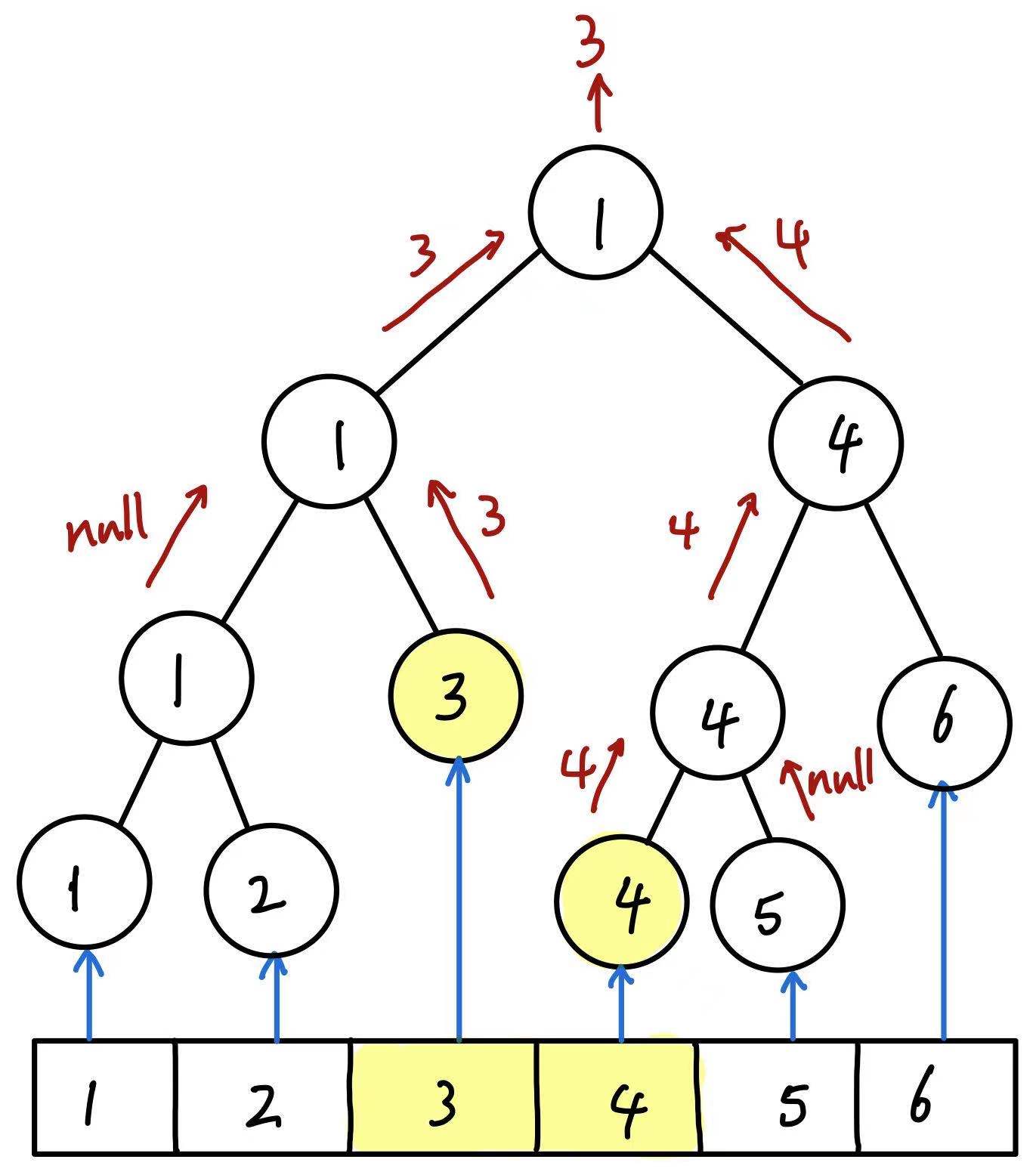
对于基于数组
Integer[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
的线段树,我们执行 queryMin(2, 3) 时函数的递归情况如下
Click to see Java Full Code
/* Segment Tree, Java */
import java.util.*;
public class SegmentTree <T extends Comparable<T>>{
public static void main(String[] args) {
SegmentTree<Integer> test = new SegmentTree<>(new Integer[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6});
System.out.println(test.dumpTree());
// test.updateTree(0, 7);
// System.out.println(test.dumpTree());
System.out.println(test.queryMin(2, 5));
}
private ArrayList<T> tree;
private T[] value;
public SegmentTree(T[] values){
this.tree = new ArrayList<>(Collections.nCopies(values.length * 2 + 1, null));
this.value = values;
this.constructTree(0, 0, values.length - 1);
}
public void updateTree(int index, T val){
this.updateTree(0, 0, this.value.length - 1, index, val);
}
public T queryMin(int l, int r){
return queryMin(0, 0, this.value.length - 1, l, r);
}
public ArrayList<T> dumpTree(){
return this.tree;
}
private T queryMin(int node, int start, int end, int l, int r){
if (this.inInterval(l, r, start, end) == 0){ return null; }
else if (this.inInterval(l, r, start, end) == 1){ return this.tree.get(node); }
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
T leftInterval = this.queryMin(this.getLChild(node), start, mid, l, r);
T rightInterval = this.queryMin(this.getRChild(node), mid + 1, end, l, r);
if (leftInterval == null){ return rightInterval; }
else if (rightInterval == null){ return leftInterval; }
else{ return this.genericMin(leftInterval, rightInterval); }
}
private void updateTree(int node, int l, int r, int index, T val){
if (l == r){
this.tree.set(node, val);
this.value[l] = val;
}
else{
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (l <= index && index <= mid){ this.updateTree(this.getLChild(node), l, mid, index, val); }
else{ this.updateTree(this.getRChild(node), mid + 1, r, index, val); }
this.tree.set(node, this.genericMin(this.tree.get(this.getLChild(node)), this.tree.get(this.getRChild(node))));
}
}
private void constructTree(int node, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) {
tree.set(node, value[l]);
} else {
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
this.constructTree(this.getLChild(node), l, mid);
this.constructTree(this.getRChild(node), mid + 1, r);
tree.set(node, this.genericMin(tree.get(this.getLChild(node)), tree.get(this.getRChild(node))));
}
}
private int getLChild(int index){ return index * 2 + 1; }
private int getRChild(int index){ return index * 2 + 2; }
private T genericMin(T o1, T o2){
if (o1.compareTo(o2) > 0){ return o2; }
return o1;
}
private int inInterval(int l1, int r1, int l2, int r2){
if (r2 < l1 || l2 > r1){ return 0; } // Intervals do not have any intersection
else if (l2 >= l1 && r2 <= r1){ return 1; } // Interval 2 complete in Interval 1
else{ return 2; } // Interval 2 partially intersect with Interval 1
}
}
问题练习
-
Leetcode 307. Range Sum Query - Mutable 非常 straight-forward 的 Segment Tree 问题 -
Leetcode 218. The Skyline Problem -
Leetcode 318. Count of Small Numbers After Self -
USACO 2020 US Open Contest, Gold Problem 1. Haircut -
USACO 2017 January Contest, Gold Problem 1. Balanced Photo -
USACO 2017 February Contest, Gold Problem 3. Why Did the Cow Cross the Road III
